资产负债表
A balance sheet, also known as a statement of financial position, is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial condition at a specific point in time. It is divided into two main sections: assets and liabilities. The balance sheet follows the fundamental accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Here’s a breakdown of the components of a balance sheet:
Assets (A) : are what the company owns (or controls). More formally, assets are resources controlled by the company as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity.
- Current Assets: These are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year. Common current assets include cash, accounts receivable (money owed to the company by customers), inventory, and short-term investments.
- Non-Current (Long-Term) Assets: These are assets that are not expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year. Common non-current assets include property, plant, equipment (PPE), investments, and intangible assets like patents and trademarks.
- Other Assets: This category may include less common assets like deferred tax assets, goodwill, and other miscellaneous assets(其他杂项资产).
Liabilities: are what the company owes. More formally, liabilities represent obligations of a company arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in a future outflow of economic benefits from the entity.Liabilities represent what a company owes to external parties. They are also typically listed in order of when they must be paid.
- Current Liabilities: These are obligations that the company is expected to settle within one year(一年内偿还的债务). Common current liabilities include accounts payable (money the company owes to suppliers), short-term debt, and accrued expenses.
- Non-Current (Long-Term) Liabilities: These are obligations that are not expected to be settled within one year. Common non-current liabilities include long-term debt, deferred tax liabilities(递延税负债), and pension obligations(养老金义务).
Equity:
Equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting its liabilities. It’s essentially the ownership interest. Common components of equity include:- Common Stock: The value of shares issued to investors.
- Retained Earnings: The accumulated profits that the company has retained (not distributed as dividends) over time. This represents the company’s ability to reinvest profits into the business.
A balance sheet should always adhere to the fundamental accounting equation. This means that the total value of assets must equal the total value of liabilities and equity.
Here’s the balance sheet equation again:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The balance sheet provides valuable information about a company’s financial health and its ability to meet its short-term and long-term obligations. By examining the balance sheet, you can assess the company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability. It’s an essential financial statement for investors, creditors, and analysts when evaluating a company’s performance.
资产负债表实例
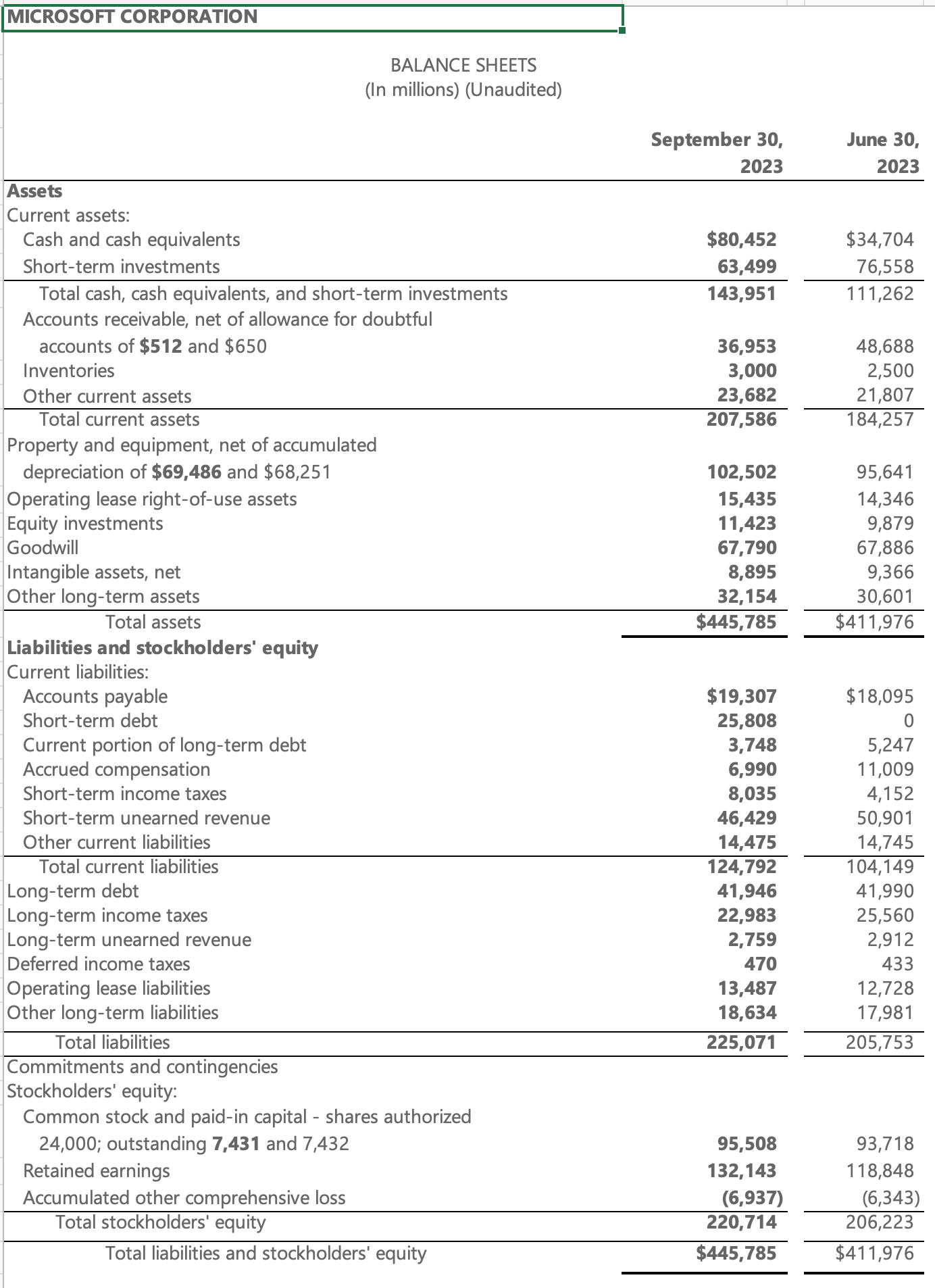
- 微软2023 Q3资产负债表
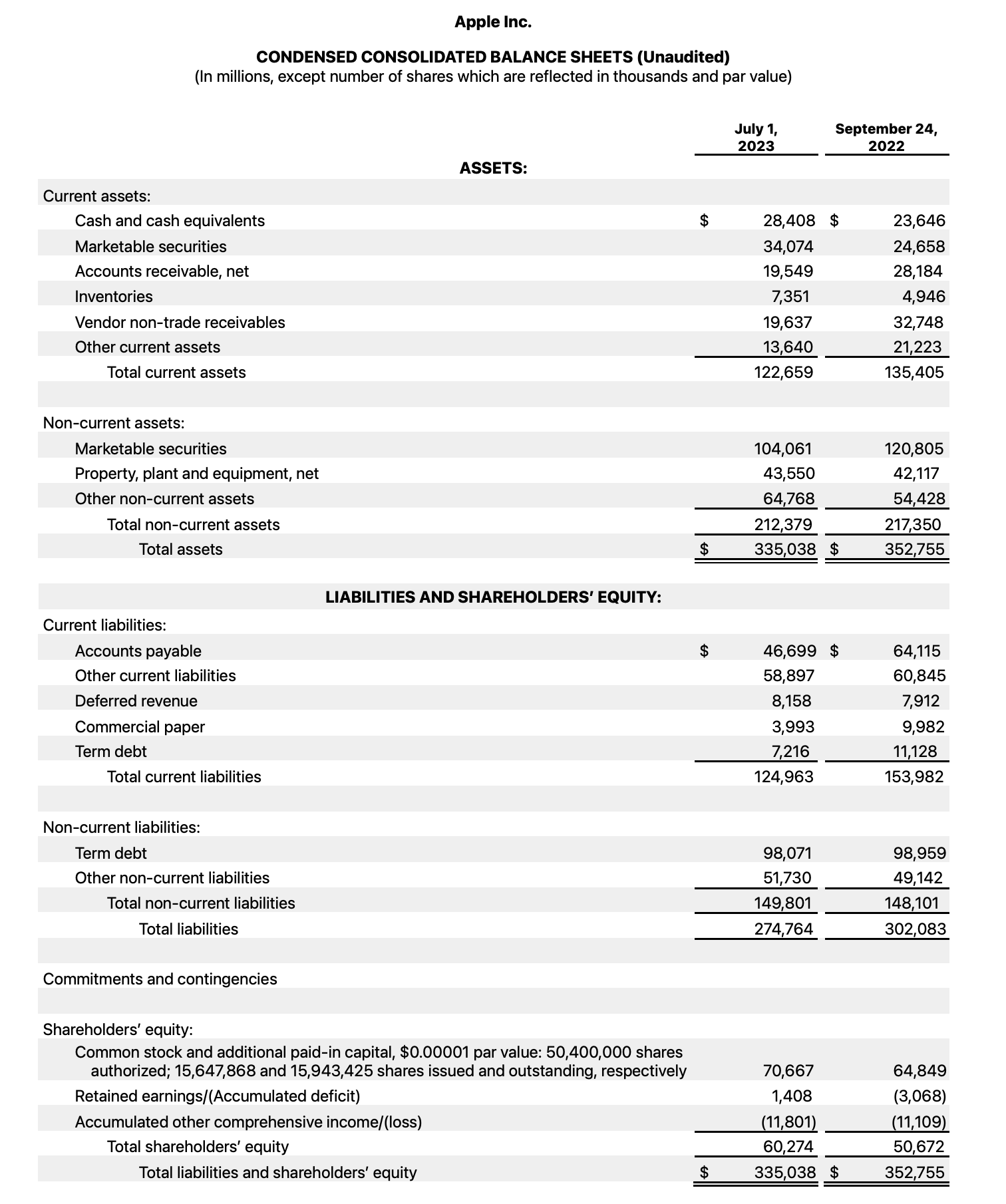
- Apple 资产负债表
通过我们对世界上最好得公司资产负债表的阅读,基本上我们可以理解资产负债表中关于A、L、E的一些定义。那么我们如何分析资产负债表呢?
资产负债表常见分析
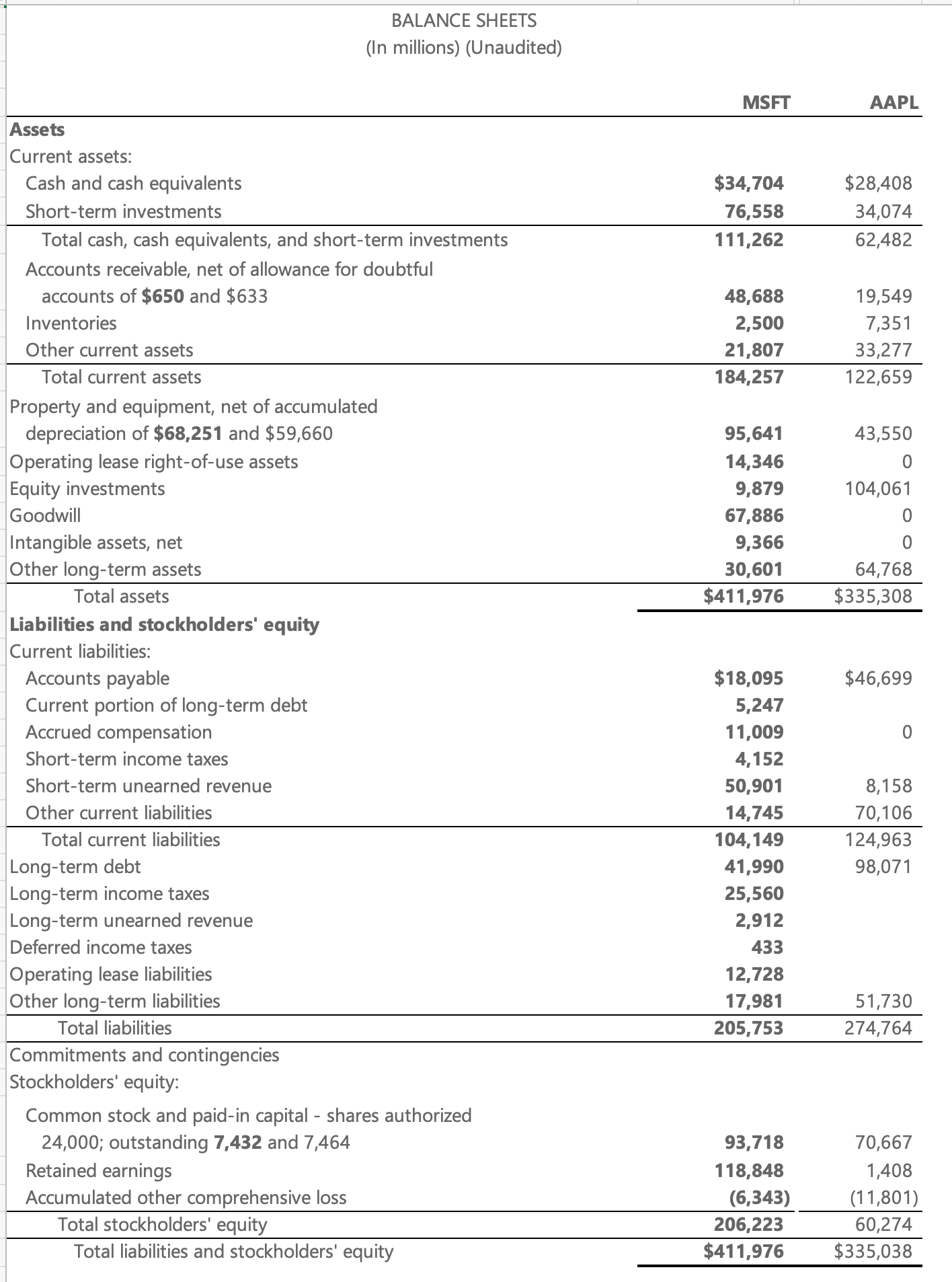
- 通过对于微软和苹果2023Q2 资产负债表得对比,我们可以了解两家公司的资产健康情况,两家都很强,但我更喜欢微软一些,微软手中有奖金1110亿美金得现金啊,这已经不是微软了,而是巨硬。
- 苹果公司是没有goodwill的,说明苹果公司很少进行收购,而微软则大举进行收购布局,比如收购领英,github等;
- 微软的存货是要远远低于苹果的,说明微软的销售更多是以service为主;
- 微软的固定资产和租赁资产远远高于苹果;
- 微软的长期债务要远远低于苹果,苹果公司太赚钱了,这家公司低息贷款都去回购股票了吧;
- 苹果的应付账款远远高于微软,说明微软是不是不缺钱?还是苹果的供应商溢价能力更高;
- 苹果的应收账款远远低于微软,说明微软好能赚钱,大家都欠微软的,哈哈哈哈;
- 微软的retained earings 远远大于苹果,说明微软为股东创造了更高的留存收益;
- 其他一些思考,现金是否大于短期债务,retained earnings 是否长期在增长,retained earnings用在哪些用途了?
资产负债表我们应该关注哪些指标
- Liquidity Ratio vs Solvency Ratio
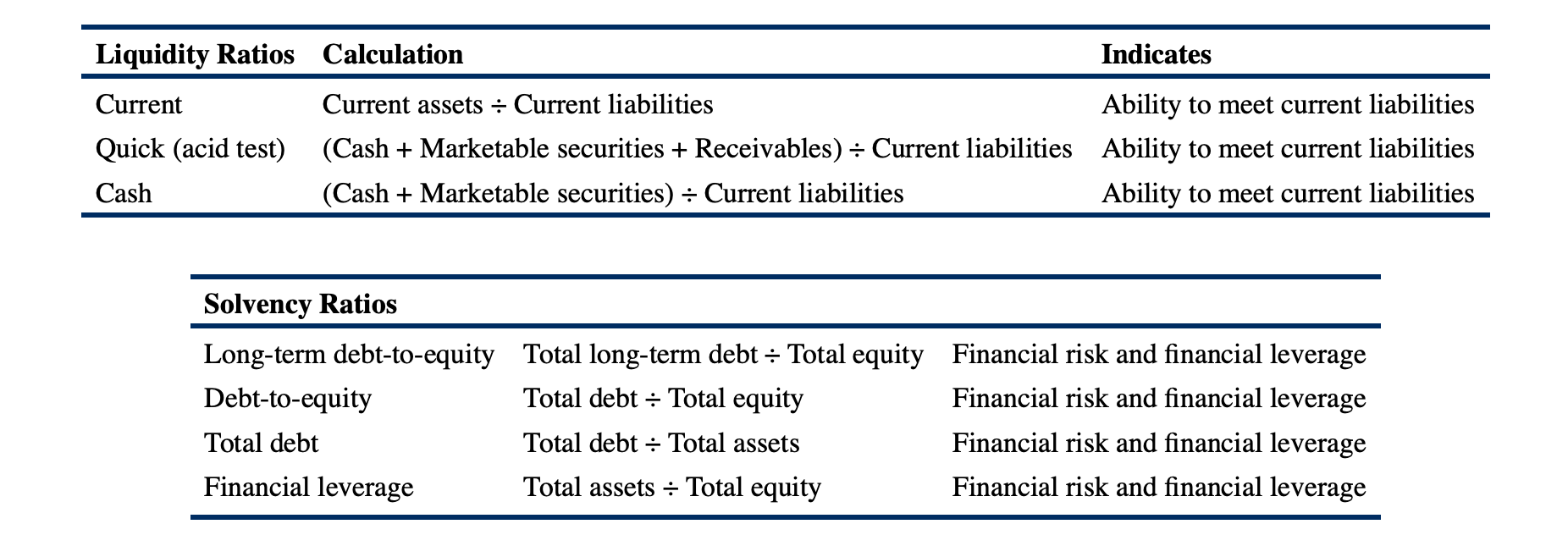
- Liquidity ratio 越大越好
- Solvency ratios 越小越好
一个好的商业模型应该满足如下三个指标:
- Times Interest Earned Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expense > 10
- Net debt / FCF < 3
- D/E < 1.5