Sampling
- 抽样方法 Sampling methods
Probability sampling method 概率抽样方法
- Sample random sampling 简单随机抽样 vs. systematic sampling 系统抽样
- 简单随机抽样:A simple random sample is a subset of a larger population created in such a way that each element of the population has an equal probability of being selected to the subset.
- 系统抽样:“With systematic sampling, we select every kth member until we have a sample of the desired size. The sample that results from this procedure should be approximately random. Real sampling situations may require that we take an approximately random sample.
- Stratified random sampling 分层随机抽样 vs. clustering sampling 聚类抽样
- 分层随机抽样(先分层,再抽样):
- In stratified random sampling, the population is divided into subpopulations (strata) based on one or more classification criteria.
- Simple random samples are then drawn from each stratum in sizes proportional to the relative size of each stratum in the population. These samples are then pooled to form a stratified random sample.
- 聚类抽样 Cluster samping:
- divide the population into clusters based on some criteria,e.g,geographic parameter.
- using sample random sampling to choose certain clusters.
- One-stage cluster smapling: all the members in each sampled cluster are included.
- Two-stage cluster sampling: a subsample is selected from each sampled cluster through random sampling.
- 分层随机抽样(先分层,再抽样):
- 概率抽样方法的图例:
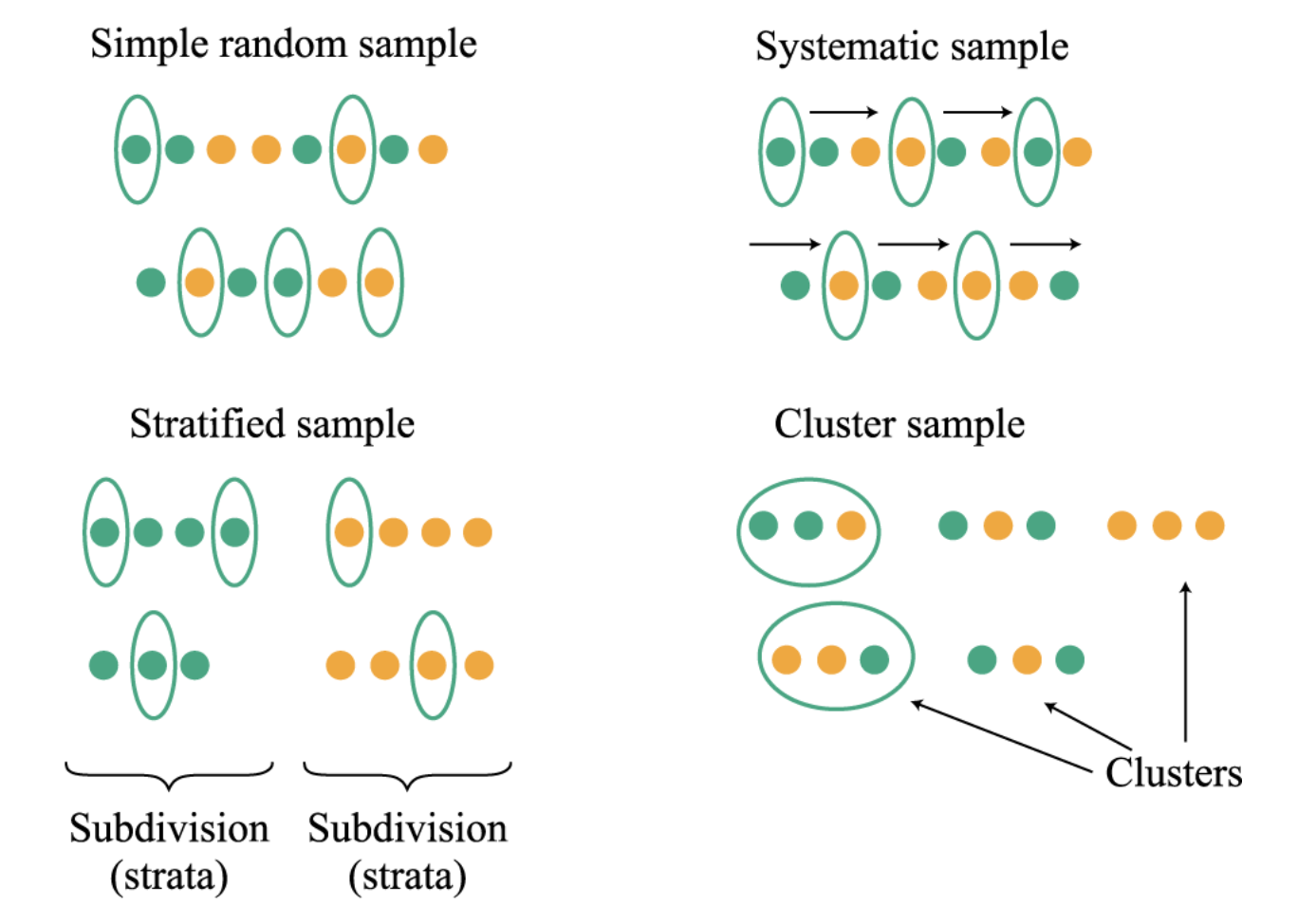
- Sample random sampling 简单随机抽样 vs. systematic sampling 系统抽样
Non-probability sampling 非概率抽样方法
- Convenience sampling 方便取样:是一种非概率抽样方法,其特点是研究者选择那些最容易获得的个体作为样本。这种抽样方法的优点是方便和快速,但其缺点是可能导致样本不够代表性,因为研究者往往选择那些容易获取的个体,而不是随机选择。
- Judgemental sampling 判断性抽样:是一种非概率抽样方法,它基于研究者的专业判断和经验,有目的地选择符合研究目的的个体作为样本。与方便抽样不同,判断抽样更注重研究者的主观判断力,以确保选取的样本能够提供对研究问题有代表性的信息。
Sampling error vs. samplng bias
- Sampling error 抽样误差:Sampling error is the difference between the observed value of a statistic and the quantity it is intended to estimate as a result of using subsets of the population.抽样误差是统计量的观测值和所要估计的真实值之间的差别。
- Sampling bias 采样偏差:是指在研究中使用的样本并不代表研究总体的情况,导致研究结果在推广到整个总体时产生误差。抽样偏差可能是由于采样方法的问题、样本选择的不恰当或者样本中某些特征的过度强调而引起的。
样本均值的分布
中心极限定理 The Central Limit Theorem
- 定义:“Given a population described by any probability distribution having mean µ and finite variance σ², the sampling distribution of the sample mean computed from random samples of size n from this population will be approximately normal with mean µ (the population mean) and variance σ²/n–>样本均值的放大 (the population variance divided by n) when the sample size n is large”
- Sampling distribution with increasing sample size

样本均值标准误差 Standard error:
- 定义:“Given a population described by any probability distribution having mean µ and finite variance σ², the sampling distribution of the sample mean computed from random samples of size n from this population will be approximately normal with mean µ (the population mean) and variance σ²/n–>样本均值的放大 (the population variance divided by n) when the sample size n is large”
- 定义:对于有一个标准差为的总体中所取出的样本计算的样本均值,其标准误差可以用下面的两个表达式来表示。样本均值的标准误差是一个在实践中应用中心极限定理时所使用的重要数据。
- 当样本总体标准差已知:
- 当样本总体标准差未知:
- 当样本总体标准差已知:
Estimation
Point Estimators
- 估计式 Estimator:
- 定义:我们用来计算样本均值和其他样本统计量的公式是估计公式,称作Estimator。
- 估计值 Estimate:“The particular value that we calculate from sample observations using an estimator is called an estimate”
- Point estimate: 根据所给定样本所计算的样本均值,它是用来作为总体均值的估计值,这个估计值被称为总体均值的点估计。
- Estimator的三个性质:
- Unbiasedness 无偏性:一个无偏估计量是指其期望值等于它所要估计的参数值。
- Efficiency 有效性:当对于同一个参数,没有其他无偏估计量具有比该估计值更小抽样分布方差时,我们就称该无偏估计量是有效的。smallest variance
- Consistency 一致性: 当样本量增大,该估计量接近总体参数真值的概率也会增大,并趋近于1.
- 估计式 Estimator:
Confidence interval estimate 置信区间估计
- Confidence interval 置信区间:
- 定义:一个置信区间是一个区间范围,我们所要估计的参数将以一个给定的概率(1-⍺,其被称作置信度)将被包含在这个区间之中。
- Significance level(⍺) 显著性水平: the probability the observations would not fall in a specific range.
- Confidence interval = Point estimate ± Reliability factor * Standard deviation
- Ponint estimate 点估计:参数的一个点估计
- Reliability factor 可靠性因子:基于点估计的假设分布和置信区间中置信度(1-⍺)的一个数
- Standard deviation 标准误:提供点估计的样本统计量的标准误
- Reliability factors for normal distribution:

- Choosing statistic for reliability factor:
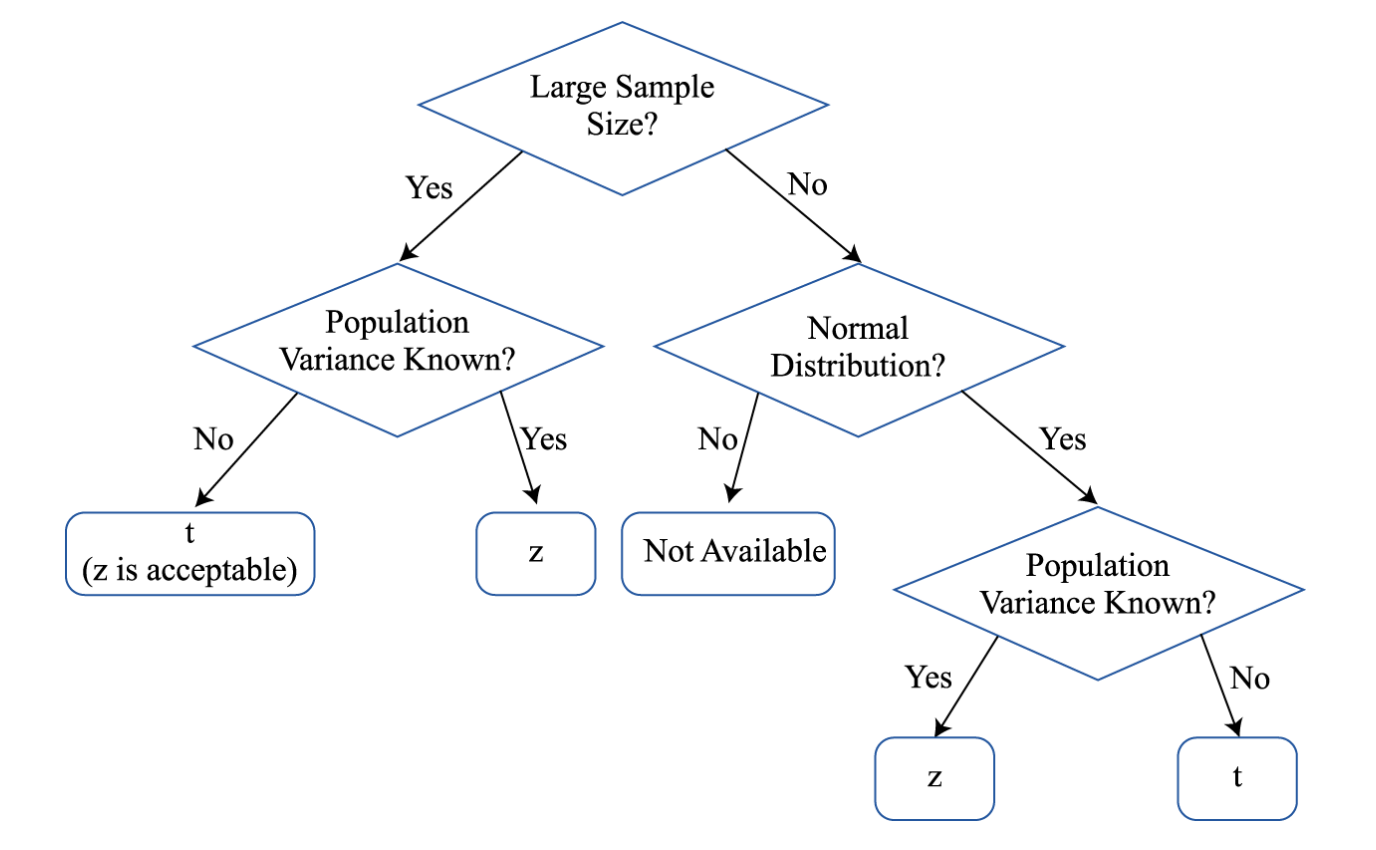
- Confidence interval of population mean with know population variance:
- Confidence interval of population mean with unknow population variance:
- Degrees of freedom(df) = n -1
- Factors on width of confidence interval
Factors Width of confidence interval Larger confidence level(1-⍺) Larger Larger significance level(⍺) Smaller Larger sample size(n,df) Smaller Larger Sample standard deviation(s) Larger t-distribution(against z-distribution) Larger - Confidence interval 置信区间:
Resampling
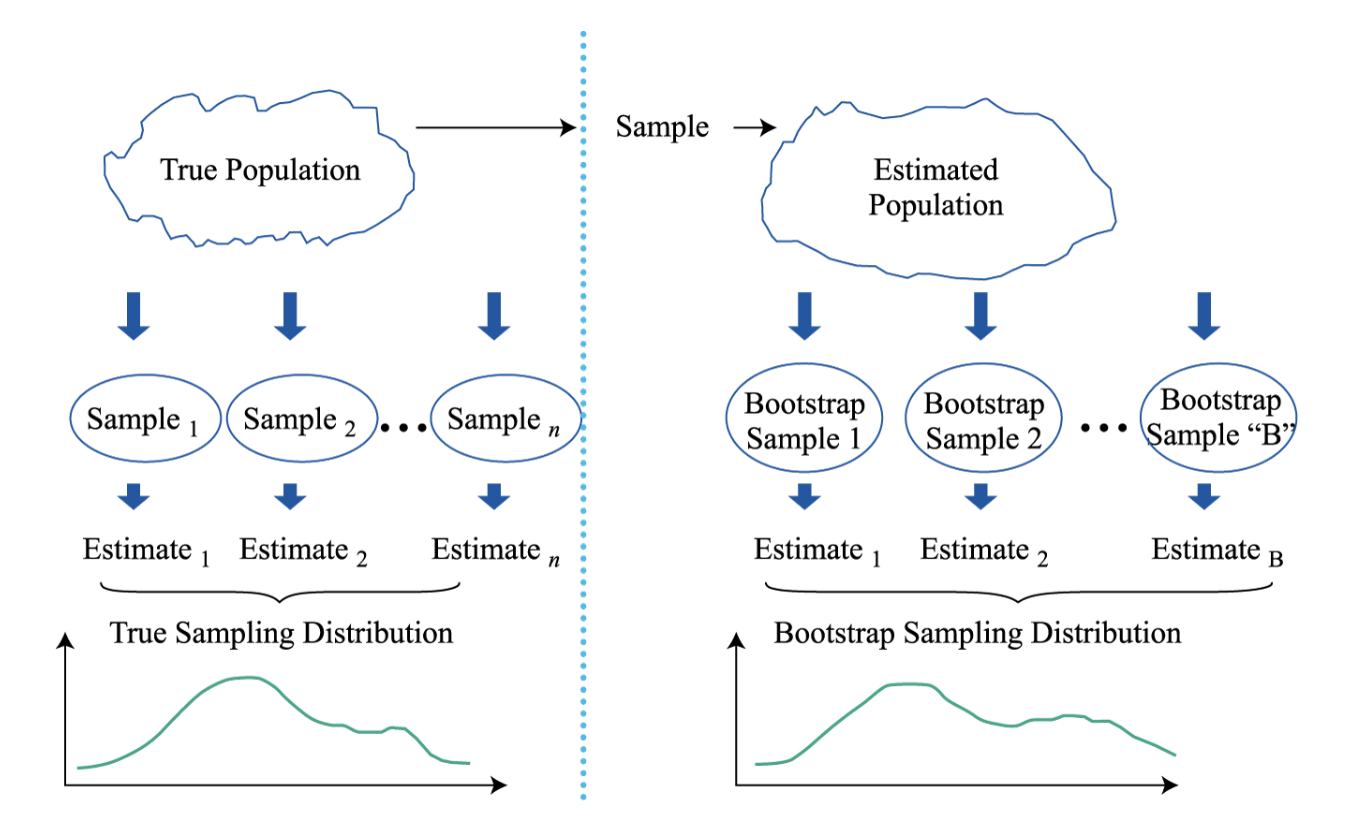
Bootstrap and jackknife are simple but powerful methods for statistical inference,and they are particularly useful when no analytical formula is available. Bootstrap constructs the sampling distribution of an estimator by repeatedly drawing samples from the original sample to find standard error and confidence interval. Jackknife draws repeated samples while leaving out one observation at a time from the set, without replacing it. Bootstrap 和 Jackknife 是简单但强大的统计推断方法,当没有可用的分析公式时它们特别有用。 Bootstrap 通过从原始样本中重复抽取样本来构建估计量的采样分布,以找到标准误差和置信区间。 Jackknife 会重复抽取样本,同时从集合中一次留下一个观察值,而不进行替换。
数据挖掘的偏差
- 数据挖掘偏差 Data-snooping bias
- 样本选择偏差 Sample selection bias
- 生存偏差 Survivorship bias
- 前视偏差 look-ahead bias
- 时期偏差 time-period bias
- 回补偏差 Backfill bias